Before we get started, I need to preface with a little bit of information. There’re many different features of switches, so many that we can never go through them in one short blog. Switches are very robust. Depending on the switch you buy, it may support a certain set of features, or it may not. It is very important to go find out what those features are that the switch supports, and make sure that it can do everything that you need it to do. Some switches even support things like routing, literally, some switches can be routers. Those are layer three switches but this post won’t cover those in particular. Instead, we’ll be focusing on the switches that your clients plug into, Access Layer Switches. These are more of a closet switch and are found at layer two.
Two Ways To Represent Switches

Logical Representation: (See above) In IT you may have seen or will see the icon above. That is a logical representation of a common Ethernet switch, you’ll see this same exact type of icon used to represent switches all over the place in diagram topology maps.
![]()
Physical Representation: (See above) Another way we can represent switches is by using a physical representation like you see above, we actually have a switch where you can see the front bezel, all of the ports, and what it physically looks like

What a Switch Provides Us With
A switch provides us with wired network access for our devices like our PCs, laptops, phones, wireless access points, printers, servers. All of these devices will plug into the Ethernet network by using a Cat5 or Cat6 cable.
Most Common Switch
The most common switch that you’re going to find and the most well-known widely used, is going to be an Ethernet switch. Ethernet is what we use to connect our users into the network. Our ethernet switches provide us with LAN access. There are other types of switches such as Fibre Channel switches for storage area networks.
Important Features
Managed vs unmanaged switch: It’s important that we have a managed switch. Having a managed switch allows us to access that switch remotely or even locally to change its configuration. An unmanaged switch does not allow us to make any changes to it and it won’t allow us to monitor it. An unmanaged switch is not something you’re going to be looking for in an enterprise or business grade network, you’re always going to want a managed switch.
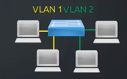
VLANs and Quality of Service (QOS): VLANs is something that you’re going to need for your enterprise grade equipment. Make sure your switches support VLANs and Quality of Service (QOS). In the diagram above we can see that we have our different types of clients connected to the network and one of those is a Voice Over IP phone.
You may be asking yourself “What in the heck does QOS do?” We need to make sure that our phone call traffic has priority over all other traffic. Why? Because we’re on the phone and if there’s any type of interruption in the traffic or if one caller gets choppy, the callers are going to notice it.
Number of Switch Ports: The number one thing that our switch provides us with is a set of ports that our host can plug into. Switches will come in a variety of 8 port, 12 port, 24 port, and 48 port. Those are the most common varieties of switches. There are others you may find out there. Usually, if you buy the little 4 port switches, usually those are managed switches. There is a common number of ports you’re going to see now why is that important? If you have a switch, you need to install into a closet that is going to support 40 computers, well you need to make sure that it has enough ports on the switch.
Speed of Ports: For hosts that are going to need to connect to common Gigabit Ethernet connectivity, then you’re going to want to make sure you buy a switch that supports Gigabit Ethernet on all of its ports, you can still find switches out there that only support Fast Ethernet on their ports. It is possible that you accidentally buy a switch that only lets you do a hundred Megabit per second instead of the Gigabit you need.
Power Over Ethernet is a technology that can be built into our switches
Power Over Ethernet: Using a Voice Over IP phone as an example, there are two different ways they can get power. One of those ways is by plugging it into the wall with the power brick, getting your power from a power outlet on the wall. The second way we can get power to our Voice Over IP phone is through something called Power Over Ethernet or POE for short. Power Over Ethernet is a technology that can be built into the switches that will allow us to power a Voice over IP phone through the cable that it is connected to.

Stacking Technology
Uplink Ports: On our switch, all the way to the right you will see a group of ports, those are uplink ports. Uplink ports will support various things. Some of the enterprise grade switches will support SFP or some type of transceiver that allows us to plug into a fiber optic cable. To be able to plug a fiber optic cable to connect our switch to the rest of the network, we need to make sure that the switch has an uplink port that supports it. Uplink ports will be able to support many different types of connections, mostly copper and fiber.
Stacking Technology: This is a technology that allows us to put multiple switches together in a stack and connect the backplane of those switches together, meaning we interconnect all the switches in such a way that they’re directly connected to the backplane. Basically, making them one big switch. If you want to do stacking, you will have to make sure you’re buying a switch that supports stacking as a technology.
Conclusion
Those are the most important features for a common Ethernet switch, and I do want to just reiterate that there are so many more features out there on switches to look out for, but as an access layer switch that’s going to be connecting our hosts into the network or clients. These are some of the most important features to look out for.
Jumpstart your IT career with NexGenT’s military-grade, remote IT training.

0 Comments